Software Architecture Concepts: Cloud Networking
Public cloud providers such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), and GCP (Google Cloud Platform) offer many network services to customers that can be configured through graphical interfaces, command line, and API endpoints. In this article, which is aimed at those who are new to the cloud and networking in general, I discuss the basic concepts you need to understand to get started with network services on AWS.
What is a network?
A network, in computing, is a group of two or more devices or nodes that can communicate. The devices or nodes in question can be connected by physical or wireless connections. The key is that there are at least two separate components, and they are connected.
What is an IP Address?
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a label used to identify a computer on a shared network. There are two versions of IP in common use today: version 4 and version 6.
IPV4
An IPv4 address is a 32-bit number that provides up to 4,294,967,296 possible addresses. Each address consists of a network identifier (which represents the network or subnet) and a host identifier (which represents the individual network-attached device).
IPV6
The size of an IPv6 address is 128 bits, compared to 32 bits in IPv4.[2] The address space therefore has 2128\=340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 addresses (340 undecillion, approximately 3.4×1038). Some blocks of this space and some specific addresses are reserved for special uses.
What is a VPC ?
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is an isolated network environment that is analogous to having a private data center in the cloud. Each VPC can connect devices using the full range of IPS of either IPV4 or IPV6.
VPC allows the creation of both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
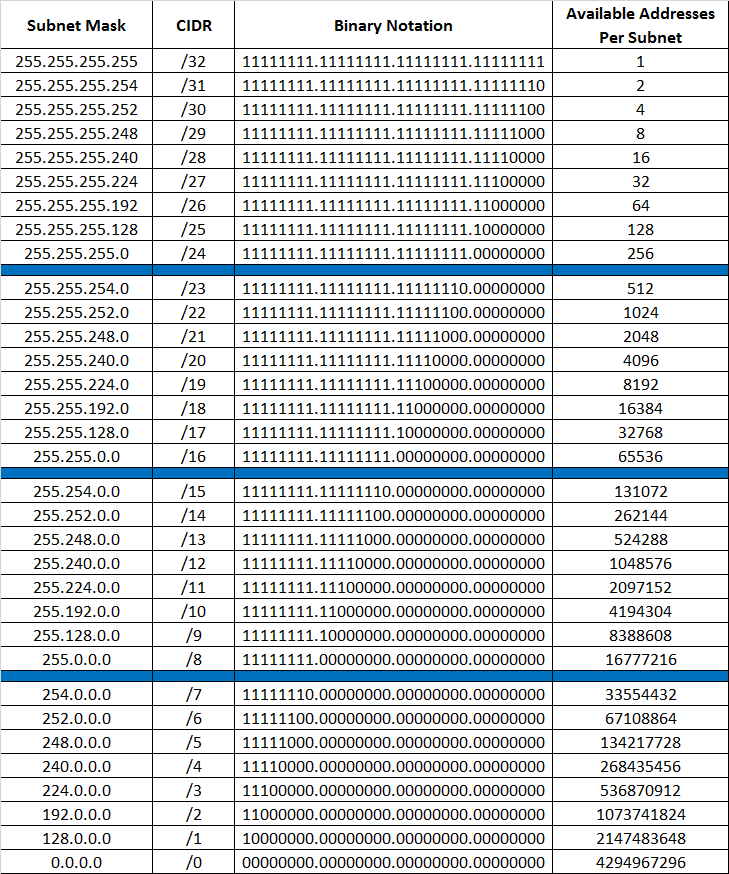
What is a Subnet?
Instead of managing the whole range of IPV4 / IPV6 address range, It is always easier to split the network range into smaller chunks that can be managed separately. these chunks are called subnets.
Take IPV4 networks for example. You can specify a fixed part of the ip, and a variable part that can be assigned to hosts, fixing a part of the IP is done with something called a network mask.
for example:
if we set the prefix length of subnet = 0 this means that all the bytes of the 32 bytes are available to be assigned to devices which means we can have 4,294,967,296 unique devices
However, if we set the mask to 24 this means we fix the first 24 bits out of the 32 bits and we end up with 8 bits (256) assignable addresses.
ex :
IP : 192.168.123.0
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0
Start IP Range: 192.168.123.0
End IP Range: 192.168.123.255
Route Tables
A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic is directed. Each subnet in a VPC must be associated to a route table. A subnet can only be assigned to one route table but a route table can be assigned to multiple subnets.
An “implicit” router is associated with all VPCs and ensures that routing works between all the subnets you create.
Each route in a route table specifies a destination CIDR and a target, and the router will use the most specific route that matches the traffic when making forwarding decisions.
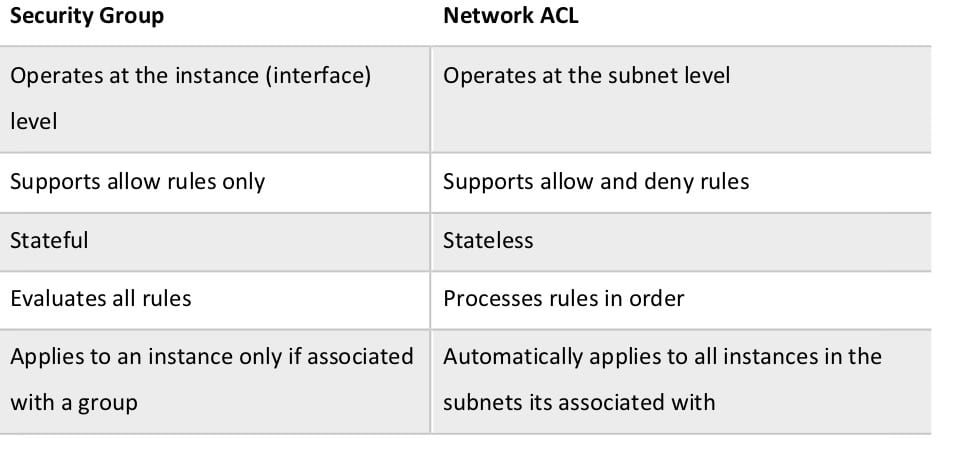
Security in VPC
There are twp main tools and services to secure your resources in your VPC.
Security Group
Network ACL (Acces Control List)
Security Group
A Security Group is an instance-level virtual firewall that controls inbound and outbound traffic. Security Groups operate on an instance (network node) level.
NACL
A Network ACL is a subnet-level firewall controlling traffic in and out of your subnets. NACL is applied on a specific subnet inside the VPC.
The difference between both tools can be summarized in :
In the next article, we will talk about connectivity with other VPCs and with the internet.
